Light amplification by stimulated emission of radiation
Lasers are an exciting advancement in the field of dentistry, now well-established in the dental armamentarium for both soft tissue and hard tissue procedures. Multiple types of dental lasers exist, each with unique properties which have significant differences in their individual benefits and limitations.
Types
Common lasers in dentistry
There are 4 common laser types in dentistry each with a unique laser-tissue interaction based on wavelength. Laser types are named after the active medium – the actual component that produces the laser energy when stimulated.
- Diode
- Nd:YAG
- Erbium
- CO2

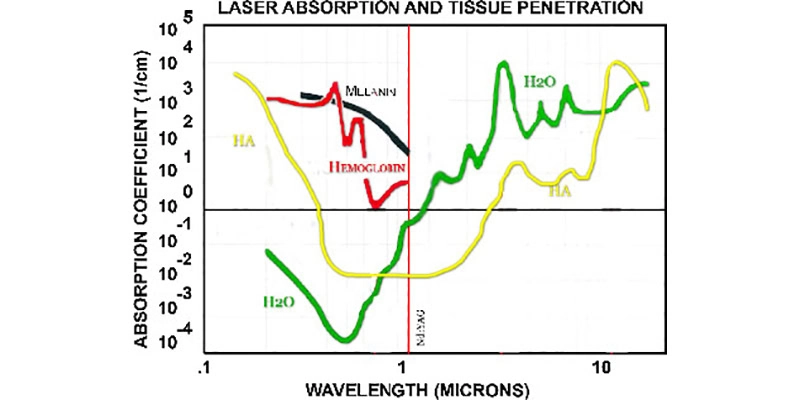
Wavelength
Light is measured in wavelengths
Each wavelength interacts with tissue differently: The 1064 wavelength passes through water and Hydroxyapatite; but is absorbed in melanin and hemoglobin. Dental wavelengths are:
- Diodes 830-1,064nm
- Nd:YAG 1,064nm
- Erbium 2,790-2,940nm
- CO2 9.3-10.6nm
Pulse
Different modes in laser dentistry
There are 4 common laser types in dentistry each with a unique laser-tissue interaction based on wavelength. Laser types are named after the active medium – the actual component that produces the laser energy when stimulated.
- Continuous
- Gated mode
- Free running pulse

Safety
Every dental laser requires attention to laser safety!
The patient, clinical staff and any observers must wear protective eyewear specific for the wavelength being used.
Laser procedures create a plume that may contain hazardous chemicals and microflora.
Scored laser tips of quartz fibers are considered sharps and need to be disposed of as such.
Warning signs need to be in a visible place and access to the operatory limited.
Schedule a practice integration consultation
Evidence-based technology



